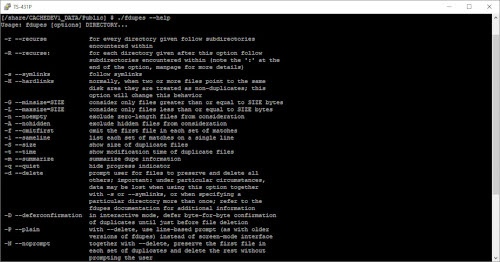
| usage |
Usage: fdupes [options] DIRECTORY…
-r –recurse for every directory given follow subdirectories
encountered within
-R –recurse: for each directory given after this option follow
subdirectories encountered within (note the ':' at the
end of the option, manpage for more details)
-s –symlinks follow symlinks
-H –hardlinks normally, when two or more files point to the same
disk area they are treated as non-duplicates; this
option will change this behavior
-G –minsize=SIZE consider only files greater than or equal to SIZE bytes
-L –maxsize=SIZE consider only files less than or equal to SIZE bytes
-n –noempty exclude zero-length files from consideration
-A –nohidden exclude hidden files from consideration
-f –omitfirst omit the first file in each set of matches
-1 –sameline list each set of matches on a single line
-S –size show size of duplicate files
-t –time show modification time of duplicate files
-m –summarize summarize dupe information
-q –quiet hide progress indicator
-d –delete prompt user for files to preserve and delete all
others; important: under particular circumstances,
data may be lost when using this option together
with -s or –symlinks, or when specifying a
particular directory more than once; refer to the
fdupes documentation for additional information
-D –deferconfirmation in interactive mode, defer byte-for-byte confirmation
of duplicates until just before file deletion
-P –plain with –delete, use line-based prompt (as with older
versions of fdupes) instead of screen-mode interface
-N –noprompt together with –delete, preserve the first file in
each set of duplicates and delete the rest without
prompting the user
-I –immediate delete duplicates as they are encountered, without
grouping into sets; implies –noprompt
-p –permissions don't consider files with different owner/group or
permission bits as duplicates
-o –order=BY select sort order for output and deleting; by file
modification time (BY='time'; default), status
change time (BY='ctime'), or filename (BY='name')
-i –reverse reverse order while sorting
-l –log=LOGFILE log file deletion choices to LOGFILE
-v –version display fdupes version
-h –help display this help message
Unless -1 or –sameline is specified, duplicate files are listed
together in groups, each file displayed on a separate line. The
groups are then separated from each other by blank lines.
When -1 or –sameline is specified, spaces and backslash characters (\)
appearing in a filename are preceded by a backslash character. For
instance, "with spaces" becomes "with\ spaces".
When using -d or –delete, care should be taken to insure against
accidental data loss. While no information will be immediately
lost, using this option together with -s or –symlink can lead
to confusing information being presented to the user when prompted
for files to preserve. Specifically, a user could accidentally
preserve a symlink while deleting the file it points to. A similar
problem arises when specifying a particular directory more than
once. All files within that directory will be listed as their own
duplicates, leading to data loss should a user preserve a file
without its "duplicate" (the file itself!).
|






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.